Android is now the world’s largest earthquake detection network
-
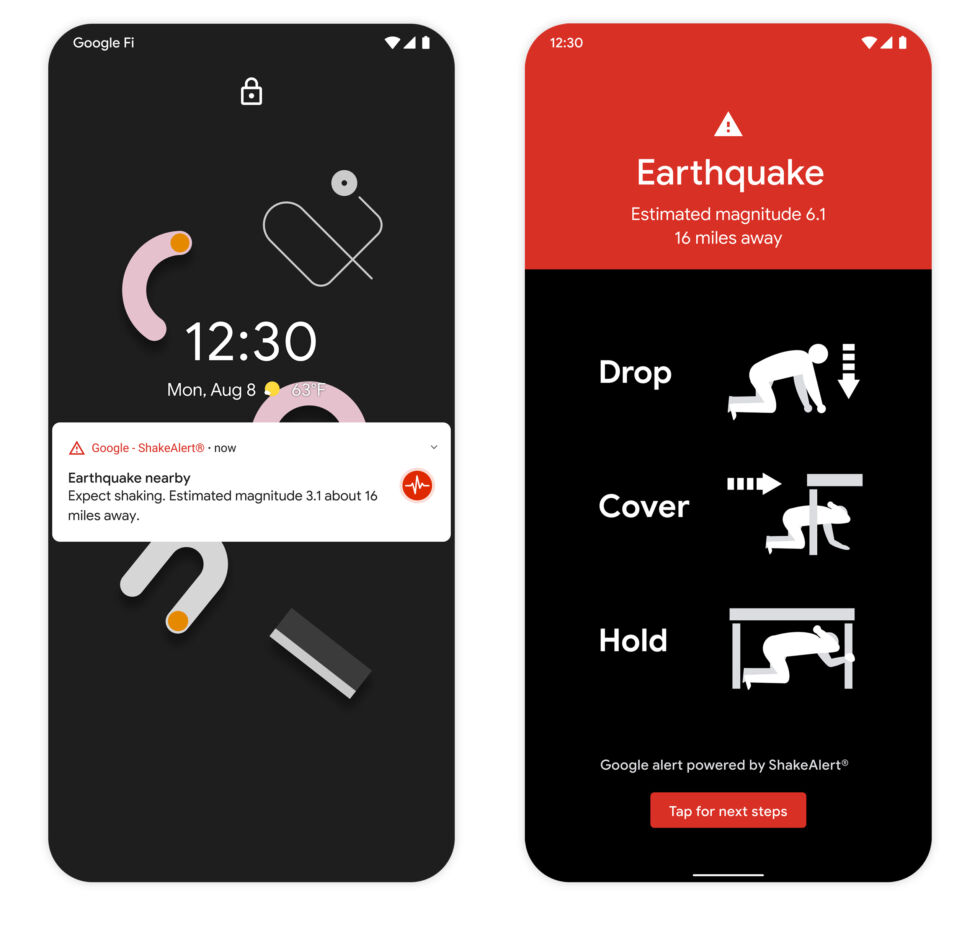
The earthquake alert system on Android, which for now is only in California. [credit: Google ]
Back in 2016, Ars reported on an interesting use for the bundle of sensors we carry around every day in our smartphones—earthquake detection. The accelerometers in your phone make a passable-enough seismometer, and together with location data and enough users, you could detect earthquakes and warn users as the shocks roll across the landscape. The University of California-Berkeley, along with funding from the state of California, built an app called "MyShake" and a cheap, effective earthquake detection network was born, at least, it was born for people who installed the app.
What if you didn't need to install the app? What if earthquake detection was just built in to the operating system? That's the question Google is going to answer, with today's announcement of the "Android Earthquake Alerts System." Google is going to build what it calls "the world’s largest earthquake detection network" by rolling earthquake detection out to nearly every Google Play Android phone. Here's the meat of the announcement:
All smartphones come with tiny accelerometers that can sense earthquakes. They’re even sensitive enough to detect the P-wave, which is the first wave that comes out of an earthquake and is typically much less damaging than the S-wave which comes afterward. If the phone detects something that it thinks may be an earthquake, it sends a signal to our earthquake detection server, along with a coarse location of where the shaking occurred. The server then combines information from many phones to figure out if an earthquake is happening. We’re essentially racing the speed of light (which is roughly the speed at which signals from a phone travel) against the speed of an earthquake. And lucky for us, the speed of light is much faster!
That "race" often works out to only a minute or so of warning, but that's usually enough to duck and cover if you catch the notification.
Read 5 remaining paragraphs | Comments
from Tech – Ars Technica https://ift.tt/31FIoPR
Comments
Post a Comment